What's The Working Principle of Ceramic Oxygen Sensors on Vehicles
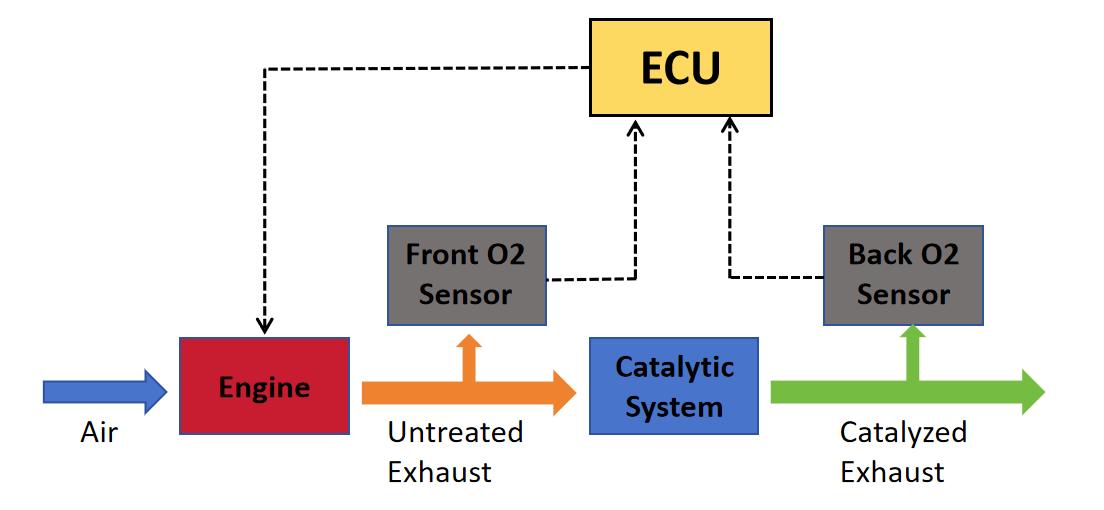
Oxygen sensors on vehicles are indispensable components, for their two main functions, one is to detect oxygen in exhaust, transmit result to ECU and control fuel injection, the other is to monitor catalytic system working, to not emit hazardous substance over limit of regulations. Therefore there at least two oxygen sensors installed on the engine, the former is front oxygen sensor and the latter is back oxygen sensors, as shown in the figure below. For some engines, more than two oxygen sensors are installed to get higher reliability, two front O2 sensors + one back O2 sensor, or even two front O2 sensors + two back O2 sensors.
Oxygen sensor on vehicles is working at high temperature, and directly contacts with corrosive gases, ceramic material is used to produce the sensor measuring chip. There are two types of ceramic material to produce measuring chip, titanium oxide (titania, TiO2) and zirconium oxide (zirconia, ZrO2). TiO2 ceramic resistance changes with variation of oxygen concentration, so the oxygen concentration can be detected by measuring TiO2 sensor chip. The chip has simple structure and chip price, but it’s too highly dependent on working temperature, therefore temperature compensation is necessary and measuring accuracy is limited.

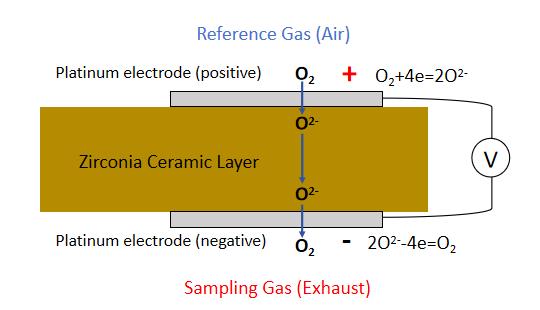
Zirconia ceramic is good conductor at high temperature, and can act as solid electrolyte when there are oxygen concentration difference, therefore it can be used to measure oxygen concentration with participation of reference gas, which shall has fixed oxygen concentration. The working principle can be described as the figure below. Platinum electrodes are mounted on the zirconia ceramic chip, reference gas (air) on one side and sampling gas (exhaust) on the other side. Oxygen in the air is 21%, while in exhaust it’s much lower. On the positive electrode, O2 molecules get electron and become oxide ions, the oxide ions move to negative electrode via the zirconia ceramic, which is conductive at high temperature. Then on the negative electrode, the oxide ions lost electrons and become O2 molecules again. Therefore oxygen is “moving” from reference gas side to exhaust side, and electromotive force (EMF) is generated between positive and negative electrodes. The higher oxygen concentration difference, the faster oxygen “moving” speed and larger EMF. By detecting the EMF, then oxygen concentration in the exhaust can be measured. The high temperature exhaust can heat up the zirconia ceramic chip, also a ceramic heater (alumina ceramic heater) can be integrated with the sensor chip to get faster start up.
Compared with TiO2 sensor, zirconia oxygen sensor has higher accuracy, faster response and longer service life, so it has wider application and higher market occupation. Globally, more than 80% oxygen sensors are supplied by Bosch, NTK&NGK, Denso and Delphi, many OEM factories produce oxygen sensors for Germany and Japanese brands vehicles as well, with outsourced or autonomous chip. ATCERA can produce zirconia ceramic chips, if need to get more information or any customized demand, please visit www.atcera.com or send email to info@atcera.com.
评论
发表评论